Real Time Geospatial (RETIGO) Frequent Questions
RETIGO is a free, web-based tool that shows air quality data that you've collected while you are stationary or in motion (walking, biking, or on a vehicle). In addition to viewing your data, RETIGO allows you to view data from nearby air quality and meteorological stations.
Below are the answers to some frequently asked questions:
- What is RETIGO for?
- Where can I get my own monitoring equipment?
- What format should my data be in?
- Can I look at someone else's data?
- How does the data repository work?
- What other data is available besides mine?
- Can I export images, graphs, or data from RETIGO?
- Does RETIGO have an API for developers?
- I know the time of my data in Eastern Standard Time.
How do I construct the timezone string for the RETIGO data file? - How can I convert my timestamp into the one that RETIGO uses?
- How does RETIGO compute averages?
- Does my data get uploaded to a central site?
- My data is tagged with latitude and longitude. Is somebody keeping track of where I go?
General
RETIGO was designed by an air pollution research group at EPA who has experience in measuring air pollution using new technologies, such as vehicles equipped with real-time air monitoring instruments. RETIGO's purpose is to support visualization and exploration of air monitoring data. While some of the custom features of the program are optimized for functions air researchers commonly desire, the input file structure does not exclude other types of geospatial time series to be viewed using the tool.
Q: Where can I get my own monitoring equipment?
Monitoring equipment ranges in price from ten dollar sensors, on up to professional grade equipment costing tens of thousands of dollars. EPA's Next Generation Air Measuring site has an array of information on emerging technologies for air monitoring.
Q: What format should my data be in?
RETIGO will read comma or space delimited plain text files. More information about the exact contents and arrangement of a RETIGO file can be found in the RETIGO Tutorials.
Q: Can I look at someone else's data?
Yes. RETIGO offers a data repository for users to share data with each other. Data files in the repository are NOT QUALITY CHECKED and are in no way endorsed or verified by the US Environmental Protection Agency. The repository is simply a service offered to RETIGO users to share data. The data in the repository is provided on an AS-IS basis.
Q: How does the data repository work?
RETIGO's data repository leverages the Environmental Sensor Data Repository (ESDR)developed by Carnegie Mellon University. When a user decides to upload data to the RETIGO data repository, it first goes to ESDR via a private, secure feed using OAuth2 authentication. If the data is valid and conforms to ESDR and RETIGO standards, an API key for the feed is automatically sent to the RETIGO server, whereupon the data file is securely downloaded from ESDR. When a user loads a data file from the repository in RETIGO, it comes directly from the RETIGO server.
Q: What other data is available besides mine?
Air quality data available from AirNow can be viewed alongside your own data. In addition, RETIGO can retrieve weather data available from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Meteorological Terminal Aviation Routine Weather Report (METAR). All data are reported hourly, and are made available by a web service in a format where RETIGO can automatically find the locations near your data and also select for the time window that matches your data. RETIGO currently offers the option of viewing:- AIRNow O3 (ozone) - AIRNow PM2.5 (2.5 micron particulate matter) - AIRNow CO (carbon monoxide) - AIRNow NO2 (nitrogen dioxide) - AIRNow SO2 (sulphur dioxide) - WMO METAR surface temperature - WMO METAR surface pressure - WMO METAR surface wind speedQ: Can I export images, graphs, or data from RETIGO?Yes and no. It is not possible to export the map image at this time, but you can export the analysis plot, timeseries plot, and wind-pollution plot.
You can also export RETIGO data into a GIS friendly format which can be read into EPA's Community-Focused Exposure and Risk Screening Tool (CFERST) or EnviroAtlas. In addition, concentration versus distance analysis data (computed by RETIGO) may be exported to a text file.Q: Does RETIGO have an API for developers?
RETIGO was created to be an end-user tool, and does not provide an Application Programming Interface (API) for developers. However, several APIs were used to create RETIGO, including:- Google Maps API - Flot API - JQuery API
Browser requirements
Q: What are the browser requirements for RETIGO?
RETIGO requires that Javascript be enabled in your browser. Also, RETIGO uses the HTML5 File API, which is supported by many browsers . RETIGO has been tested and shown to work correctly using Firefox 21.0, Chrome 27.0, and Opera 12.15.
Data file format
Q: I know the time of my data in Eastern Standard Time.
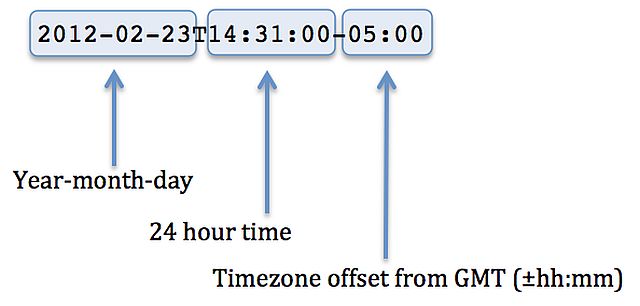
How do I construct the timezone string for the RETIGO data file?RETIGO files use an international standard for referencing dates and times called UTC/ISO 8601. The reason for the standard is to provide an unambiguous and well-defined representation of dates and times, and to avoid the possibility of misrepresenting time. Although the timestamp is based in GMT, it is easy to "think" in terms of a particular time zone by using a GMT offset. For example, suppose a datapoint was taken at 2:31pm on February 23, 2012, in Eastern Standard Time. Since EST lags GMT by 5 hours, the corresponding UTC/ISO 8601 timestamp would be 2012-02-23T14:31:00-05:00
Q: How can I convert my timestamp into the one that RETIGO uses?
A tool called the timestamp converter is provided which can convert several popular formats into the UTC/ISO 8601 format that RETIGO uses.
Q: How does RETIGO compute averages?
By default, RETIGO shows you a time-averaged view of your data. (You can also view the raw data by using "Block Mode"). The amount of averaging is dependent upon the size of your data, with larger files requiring more averaging than smaller ones. Typically, enough points are averaged together such that the resulting averaged dataset contains about 1000 points. For example, if your dataset contains about 50,000 points, every 50 points would be averaged together. The data is first sorted by the ID field, then each batch of IDs is sorted by time. Successive points in time are then block-averaged using a simple statistical mean. Different IDs are never averaged together, allowing you some control over the averaging process.
Privacy
Q: Does my data get uploaded to a central site?
Not unless you explicitly decide to upload it. When you view a data file in RETIGO, the data never leaves your computer and is not uploaded to a central site. It is simply read into your computer's memory and displayed using EPA's custom Javascript program running in your web browser. If you want to share your data with other users, you can upload it using the RETIGO Data Repository tool.
Q: My data is tagged with latitude and longitude. Is somebody keeping track of where I go?
No. Although your data must include the time, latitude, and longitude in order to provide geospatial and temporal context, that information never leaves your computer unless you explicitly decide to upload your data. Even then, the data is anonymous and is not associated in any way with you or your IP address. .
