National Enforcement and Compliance Initiative: Protecting Communities from Coal Ash Contamination

EPA is committed to reducing pollution from coal ash, also known as coal combustion residuals or CCR, the toxic material left behind after facilities burn coal for energy. Coal ash contains contaminants known to cause cancer and other serious health effects. Coal ash surface impoundments exist in all parts of the country and create significant environmental and public health risks for nearby residents.
Problem
In 2021 alone, coal-fired electric utilities generated almost 80 million tons of coal ash. There are approximately 300 regulated coal facilities nationwide that currently house approximately 775 coal ash surface impoundments and landfills. Coal ash disposal impoundments and landfills are found throughout the country in both urban and rural areas. Of these facilities, 119 are located near communities identified as already overburdened by pollution.
The harm to human health and the environment from noncompliance with EPA’s Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Coal Ash Program can be significant and can occur through catastrophic releases of contaminants into the air or contamination of groundwater, drinking water, or surface water. These impacts have and will continue to be felt by surrounding urban and rural communities until the coal ash is properly contained, controlled and cleaned up.
Goals
The Protecting Communities from Coal Ash Contamination National Enforcement and Compliance Initiative or NECI seeks to identify and meaningfully reduce the most significant risks to air quality, drinking water, surface waters, and groundwater resources, from coal ash disposal.
FY 2024 RESULTS
In fiscal year (FY) 2024, EPA substantially increased enforcement resources for the coal ash program and assessed over 100 units for compliance with the coal ash rules. In addition, EPA finalized six settlement agreements. The agency continues to:
- Negotiate compliance actions that are meaningful to communities,
- Advance toward further assessment and cleanup groundwater through enhanced monitoring and refined corrective measures, and
- Ensure proper closure of coal ash units to protect public health and the environment.
In addition, the agency’s work to return facilities to compliance and increase transparency includes requirements that documents posted to publicly accessible facility compliance websites are revised for accuracy and completeness.
Enforcement Cases
In FY 2024, EPA completed agreements/final orders and settlement agreements with five companies to resolve violations of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act coal ash regulations. The orders and agreements address noncompliance at facilities located in New York, Alabama, Pennsylvania, Colorado and Puerto Rico, and require companies to take certain actions including addressing groundwater monitoring issues, conducting effective and protective groundwater cleanup, addressing emergency planning, and paying a fine. Enforcement accomplishments include:
Greenidge Generation LLC: In January 2024, EPA finalized a compliance agreement/final order resolving violations at the company’s Greenidge, New York gas-fired power plant (formerly a coal burning power plant). The agreement requires Greenidge to address groundwater monitoring issues and ensure proper closure under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of a surface impoundment containing over 600 million pounds of coal ash. The company has also paid a civil penalty of $105,000. (Read EPA Settlement with Greenidge to Address Noncompliance with Coal Ash Regulations press release)
AES Puerto Rico, L.P.: In September 2024, EPA finalized a settlement with AES Puerto Rico, L.P. (AES), regarding an electrical generating plant in an overburdened community in Guayama, Puerto Rico. Under the settlement, AES will address groundwater monitoring issues and to ensure proper reporting on its coal ash landfill under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. The company has also paid a civil penalty of $71,845. (Read the Settlement with AES Puerto Rico, L.P. press release. El comunicado está disponible en español).
Keystone-Conemaugh Projects, LLC: In September 2024, EPA finalized a settlement with Keystone Conemaugh Projects, LLC (“KEY-CON”), which operates the Conemaugh Generating Station in New Florence, Pennsylvania. The settlement commits KEY-CON to ensure compliance with coal ash regulations at its four coal ash surface impoundments, including properly monitoring and remediating groundwater, if necessary. KEY-CON will pay a civil penalty of $185,927. (Read EPA settles with Keystone-Conemaugh Projects, LLC press release.)
Alabama Power Company: In September 2024, EPA finalized a settlement with Alabama Power Company (Alabama Power), to resolve alleged violations of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act’s coal ash regulations at the James M. Barry Electric Generating Plant located in Bucks, Mobile County, Alabama. The settlement requires Alabama Power to evaluate and expand its groundwater monitoring program associated with its coal ash surface impoundment, review and upgrade its Emergency Action Plan, and to pay a civil penalty of $278,000. (Read the Settlement with Alabama Power Company press release.)
Public Service Company of Colorado: In September 2024, EPA finalized a settlement with Public Service Company of Colorado (PSCo), which operates the Cherokee Station electrical generating plant in an overburdened community in Denver, Colorado. The settlement requires PSCo to address groundwater monitoring deficiencies, conduct effective and protective groundwater cleanup, and pay a penalty of $134,500. Specific actions required under the settlement include developing and implementing a remedy addressing releases of lithium above regulatory levels and contaminated groundwater of approximately 1.3 million cubic yards from coal ash surface impoundments that were closed in 2017. (Read EPA Settles with PSCo press release.)
Enforcement Alerts
In December 2023, EPA issued an enforcement alert titled, “EPA Finds Significant Noncompliance with RCRA Coal Ash Disposal Regulations.” The alert informs regulated entities of common compliance issues related to closure and groundwater remediation requirements.
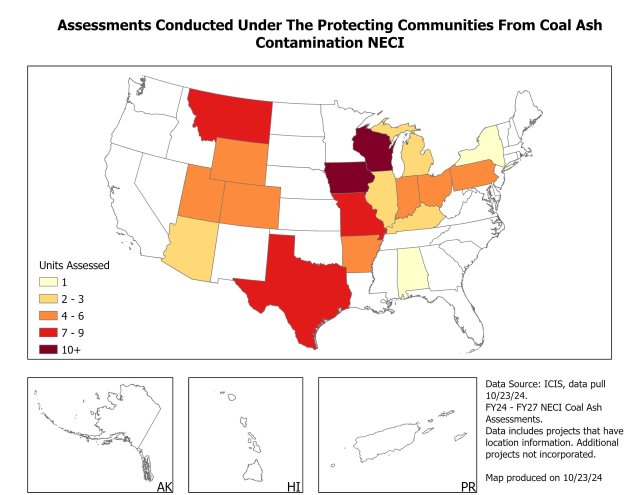
Compliance Assessments
In FY 2024, EPA completed compliance assessments of 107 coal ash units, including onsite inspections, to determine compliance with coal ash regulations.
The types of significant compliance issues identified in these compliance assessments are the same as those discussed in the above referenced Enforcement Alert.
Capacity Building Efforts
In FY 2024, EPA trained and educated staff that are responsible for enforcing the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act RCRA’s coal ash regulations. EPA hosted five Coal Ash Program training sessions with a combined total of over 400 participants: Topics covered included a basic overview of the Coal Ash program and regulations, litigation related to the CCR Rule, and criminal enforcement authorities.
